
Additionally, control assertions he may not, for example, perform existence-related procedures such as sending vendor confirmations. So knowing the risk of material misstatement at the assertion level is critical. Company executives are required to make assertions or claims to the public regarding certain aspects of a business.
Testing Controls in an Audit of Internal Control
9The SEC Advisory Committee on Smaller Public Companies considered a company’s size with respect to compliance with the internal control reporting provisions of the Act. See Advisory Committee on Smaller Public Companies to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, Final Report, at p. 5 (April 23, 2006). Below are some examples which provide an indication, but not an exhaustive list of how assertions can be tested at FAU and AA. Rights and obligations – means that the entity has a legal title or controls the rights to an asset or has an obligation to repay a liability. Accuracy – this means that there have been no errors while preparing documents or in posting transactions to ledgers. The reference to disclosures being appropriately measured and described means that the figures and explanations are not misstated.
Forming an Opinion

Financial statements have financial statement level risks such as management override or the intentional overstatement of revenues. For example, the intentional overstatement of revenues has a direct effect upon the existence assertion for receivables and the occurrence assertion for revenues. Therefore, even when you identify financial statement level risks, consider whether they might affect assertion level risks as well.
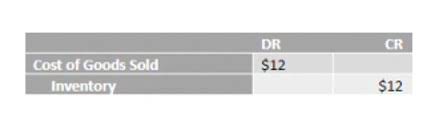
Testing Controls
- Rather than using an inefficient approach—let’s audit everything—the auditor pinpoints audit procedures.
- The auditor’s strategy may or may not include testing the operating effectiveness of controls.
- Some people may refer to these as audit assertions as they are evaluated during an audit of an entity’s financial statements.
- Management assertions form the bedrock upon which auditors assess the financial statements of a company.
- Further, control activities relevant to the audit include those control activities that the auditor judges necessary to understand in order to assess the risks of material misstatements at the assertion level.
- When a significant risk is present, the auditor should perform procedures beyond his or her normal approach.
In addition to the financial data under review, auditors also consider the actual financial statements to ensure they are clear, include the appropriate related disclosures, and are formatted in accordance with accounting standards and the law. The valuation or allocation assertion concerns the accuracy and appropriateness of the recorded values for assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses. Auditors assess whether the values retained earnings balance sheet assigned to items in the financial statements are in accordance with applicable accounting standards and reflect their fair value. The requirements in this appendix supplement the requirements of this standard.
At the end of this article, you can also see the summary of all assertions and their usages. 1See paragraph .B15, for further discussion of the evaluation of the controls over financial reporting for an equity method investment. Cut–off – that transactions are recorded in the correct accounting period. Relevant test – reperformance of calculations on invoices, payroll, etc, and the review of control account reconciliations are designed to provide assurance about accuracy. Sufficient and appropriate disclosures have been made on related transactions, events and account balances.
- This helps ensure that the financial statements in question comply with accounting standards and regulations.
- The preparation of financial statements is the responsibility of the client’s management.
- Auditors assess whether the values assigned to items in the financial statements are in accordance with applicable accounting standards and reflect their fair value.
- 18/See Appendix C, which provides direction on modifications to the auditor’s report that are required in certain circumstances.
- Auditors often assess control risk at high because they don’t plan to test for control effectiveness.
Our Auditing Services
When it comes to account balances, management is responsible for https://www.bookstime.com/ making several assertions. Existence asserts that assets, liabilities, and equity interests exist at a given date. Rights and obligations assertion states that the entity holds or controls the rights to its assets and has obligations to settle its liabilities.
